| METHOD: | Grand-canonical transition-matrix Monte Carlo [1] and histogram re-weighting |
| V/σ3: | 512 |
| TRUNCATION: | 3σ + standard long range corrections |
| Prob. of Disp. Move: | 0.75 |
| Prob, of Ins/Del. Move: | 0.25 |
| Biasing Function Update
Frequency |
1.0E6 trials |
| Simulation Length: | 8.0E9 trials |
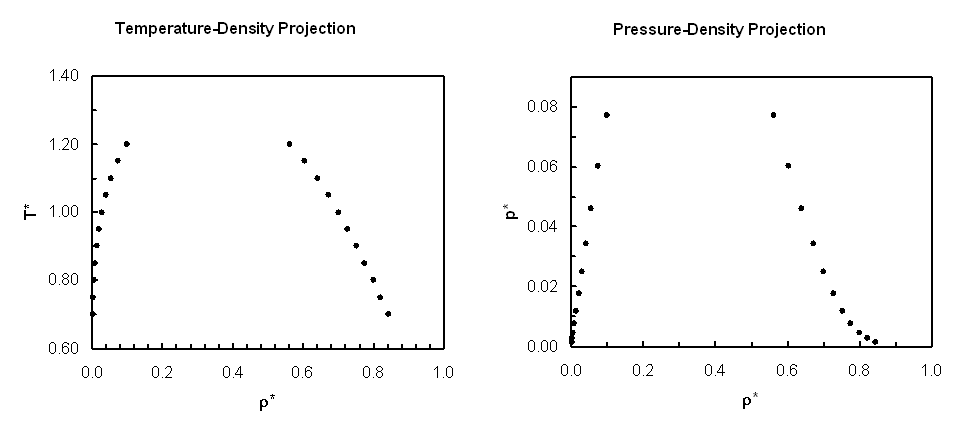
Liquid-Vapor Phase Coexistence Properties:
| T* | ρvap* |
+/- | ρliq* | +/- | psat* | +/- | Uvap* | +/- | Uliq* | +/- | ln zsat | +/- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.70 | 1.99600E-03 | 1.42E-06 | 8.43739E-01 | 2.15E-04 | 1.36959E-03 | 9.51E-07 | -2.50042E-02 | 3.32E-05 | -6.10256E+00 | 1.83E-03 | -6.25715E+00 | 4.64E-04 |
| 0.75 | 3.62958E-03 | 1.05E-06 | 8.21911E-01 | 2.68E-04 | 2.63525E-03 | 6.61E-07 | -4.24954E-02 | 2.12E-05 | -5.90799E+00 | 1.73E-03 | -5.68312E+00 | 4.31E-04 |
| 0.80 | 6.09962E-03 | 2.70E-06 | 7.99867E-01 | 2.70E-04 | 4.64539E-03 | 1.29E-06 | -6.75763E-02 | 6.18E-05 | -5.71605E+00 | 1.87E-03 | -5.19614E+00 | 3.53E-04 |
| 0.85 | 9.64024E-03 | 2.73E-06 | 7.76854E-01 | 2.62E-04 | 7.63583E-03 | 1.77E-06 | -1.01924E-01 | 5.45E-05 | -5.51841E+00 | 1.98E-03 | -4.77887E+00 | 6.41E-05 |
| 0.90 | 1.45128E-02 | 3.91E-06 | 7.52806E-01 | 1.19E-04 | 1.18493E-02 | 2.17E-06 | -1.47396E-01 | 3.70E-05 | -5.31647E+00 | 9.20E-04 | -4.41897E+00 | 3.02E-05 |
| 0.95 | 2.10228E-02 | 5.63E-06 | 7.27724E-01 | 2.03E-04 | 1.75374E-02 | 3.71E-06 | -2.06003E-01 | 8.41E-05 | -5.11032E+00 | 1.57E-03 | -4.10680E+00 | 1.55E-04 |
| 1.00 | 2.95686E-02 | 7.33E-06 | 7.01018E-01 | 9.55E-05 | 2.49576E-02 | 4.83E-06 | -2.80550E-01 | 1.13E-04 | -4.89568E+00 | 4.10E-04 | -3.83428E+00 | 1.11E-04 |
| 1.05 | 4.06547E-02 | 9.12E-06 | 6.72152E-01 | 1.14E-04 | 3.43602E-02 | 6.93E-06 | -3.74433E-01 | 7.62E-05 | -4.66955E+00 | 6.91E-04 | -3.59507E+00 | 9.92E-05 |
| 1.10 | 5.50768E-02 | 8.88E-06 | 6.40799E-01 | 1.19E-04 | 4.60204E-02 | 6.58E-06 | -4.93412E-01 | 1.40E-04 | -4.43069E+00 | 9.16E-04 | -3.38410E+00 | 7.07E-05 |
| 1.15 | 7.41176E-02 | 8.93E-06 | 6.05204E-01 | 9.15E-05 | 6.02112E-02 | 7.40E-06 | -6.46777E-01 | 1.45E-04 | -4.16818E+00 | 6.97E-04 | -3.19707E+00 | 5.92E-05 |
| 1.20 | 1.00339E-01 | 3.00E-05 | 5.63158E-01 | 5.22E-05 | 7.72251E-02 | 1.42E-05 | -8.55172E-01 | 2.95E-04 | -3.87120E+00 | 4.56E-04 | -3.03072E+00 | 7.61E-05 |
Remarks:
Uncertainties were obtained
from 5 independent simulations and represent 67% confidence limits (one
standard deviation).
Liquid-vapor coexistence was determined by adjusting the activity such
that the pressures of the liquid and vapor phases were
equal. Here, the pressure is not the conventional virial pressure [2,
3] but is the actual thermodynamic pressure, based on the
fact that the absolute free energies can be obtained from the
distributions determined from simulation [4]. Alternative methods, for
example Gibbs-ensemble Monte Carlo and combination grand-canonical
Monte Carlo and histogram re-weighting, can be used to determine
liquid-vapor coexistence. A review of standard methods of phase
equilibria simulations can be found in Ref. 5.
As introduced in Refs. 2 and 3, the activity, z, is defined as
z = Λ-3 exp(βμ)
where Λ is the de Broglie wavelength, β = 1/(kBT)
(where kB is Boltzmann's constant),
and μ is the chemical potential. It is sometimes more convenient to
work with ln z in the simulations and in post-processing.
Phase-coexistence energies were obtained by determining the
mean potential energy at a given value of N for an additional 8 billion
MC trials. Combining this information with the particle number
probability distribution, the mean potential energy of the coexisting
phases can be calculated [6].
[1] J. R. Errington, J. Chem. Phys. 118,
9915 (2003).
[2] M. P. Allen and D. J. Tildesley, Computer
Simulation of Liquids
(Oxford University Press, New York, 1989).
[3] D. Frenkel and B. Smit, Understanding
Molecular Simulation, 2nd ed.
(Academic, San Diego, 2002).
[4] J. R. Errington and A. Z. Panagiotopoulos,
J. Chem. Phys. 109, 1093
(1998).
[5] A. Z. Panagiotopoulos, J. Phys.: Condens.
Matter 12, 25 (2000).
[6] J. R. Errington and V. K. Shen, J. Chem. Phys. 123, 164103 (2005).